One of the most crucial elements of conducting any kind of research is DATA.
It is the soul of the research. Every good research begins with collecting the right kind of data. And without it, you cannot even proceed one step in your research.
So, it will not be wrong to say that DATA is the ENGINE of your RESEARCH that keeps it going!
Whether you are working on some school assignment, conducting a business study or even working on a professional report. Your research depends greatly on the collection of data. And its quality depends on the quality of the data, too.
This is exactly where the type of data matters, primary or secondary.
Oh no, do not get confused, there are two types of data that you can collect for your research. Although they are serving the same purpose. But the approach to collecting data is totally different.
Don’t worry, you will learn all the key difference between primary and secondary research right here. As learning this difference is the key to choosing the right method for data collection. This ultimately leads to better interpretation and results.
In the world of research, both types of data play very different roles.
Primary research is all about collecting first-hand information from people, events, or experiments. It involves collecting all the data by yourself. Thus, it is completely original, authentic, and tailored to your specific research goals. You do not need to worry about validating it.
On the other hand, secondary research is just the opposite. It is all about the data that already exists. So, you do not need to collect it by yourself. But you can extract it from the books, articles, reports, or any other sources.
Yeah, it is exactly the one available on the Internet.
But the interesting fact is that both of them are useful. You cannot say which one is better. But it depends entirely on the scope of your research.
Well, that is the problem that we are going to address through this blog.
These two types of data collection often confuse the researchers about which one they should use for their study. Obviously, the data is the foundation of any research. And selecting the wrong one can influence the research badly.
That is why this blog will help you understand the key difference between primary and secondary research. This will help you choose the right method for your research. From defining these terms in simple words to explaining how each of these works. You will learn everything that you need to know for choosing the right research method.
So, are you ready to embark on the journey for primary vs secondary research? Let us get started right now!
What Is Primary Research?
Let us start our journey by understanding what primary research really is.
Primary research is defined as the kind of data that is collected directly by the researcher for a specific study or purpose. That means that the information does not exist at the moment. So, the researcher has to gather it from scratch.
Primary research is sometimes regarded as more accurate, reliable, and relevant to a specific research question because the researcher gathers it themselves.
Key Characteristics of Primary Research
Here are some key features of primary research that make it unique. So, let us take a look at them briefly:
- First-hand information: The information is obtained first-hand from the people, experiment, or observation.
- Highly specific: It is created to respond to the specific question you want to answer.
- Authentic and original: The information is newly gathered, so it is not subject to past prejudice and interpretation.
- Time-consuming: It is hard, time-consuming, and even costly to collect your own data.
- Flexible: You are able to modify your questions, sampling approach, or method depending on what you need to research.
These exclusive features make primary data quite useful in cases where the correctness and reliability of data matter a lot.
Common Methods of Primary Research
I know you must be wondering how such data is collected. Well, the researchers use various types of methods to collect primary data for their research. Here are the most common ones for you:
Researchers use many methods to collect primary data. Here are the most popular techniques:
1. Interviews
One of the most common process of primary data collection is interview. It is a process of inquiring an individual or group of people. It may be face-to-face or by phone or Internet. So, this approach will assist you in collecting in-depth and personal data.
2. Surveys and Questionnaires
The next one is surveys or questionnaires. They enable you to gather information of so many people without any hassle.
So, they are frequently applied in academic research practices since they provide quantifiable outcomes. The questions may either be open-ended (qualitative) or closed-ended (quantitative).
Thus, it can provide both qualitative and quantitative data sources.
3. Observations
In this technique, the researcher observes and notes down the behaviours, actions or events closely. It is applied in the field of psychology, education, and social sciences.
4. Experiments
The experiment is another common data collection technique for primary research. It involves changing variable and then observing its impact.
This technique is specifically useful in science and engineering fields.
5. Focus Groups
A focus group is a small group of individuals who are discussing a product or a topic. It is used by researchers to know opinions, attitudes, and motivations.
So, all of these data collection techniques helps researchers in collecting both qualitative and quantitative data. All you need to do is align it with the aim and purpose of your study.
Example of Primary Research
Nothing can make things more clearer than an example. So:
Suppose a university is aiming to enhance its student services. Therefore, to understand what students really need, the staff might conduct a “Student Satisfaction Survey.”
They prepare questions carefully and send them to the students directly to get responses. It is a perfect example of collecting primary data as university is gathering original data directly from its students.
Why Primary Research Matters?
Primary research is necessary as it provides the researchers with total control over the data. What to collect, by what means to collect, and by whom to collect is up to you. So, this is what makes your findings very accurate and powerful enough to make academic or business decisions.
Hence, it might consume more time and resources. But the advantages usually justify the efforts.
What Is Secondary Research?

Now, let us talk about the secondary research.
Well, yeah, you guessed it right. This research is the one that we most commonly use in assignment writing.
So, secondary research is the use of data that has already been gathered, documented, and published by other individuals or entities. Thus, you do not need to collect new information by yourself, but use the available sources like books, articles, reports, and online publications. This helps researchers in understanding the topic before diving deep into it.
The basic idea behind the concept of secondary research is that someone has already collected all the data that you need. All you need to do is find it and analyze it for your study.
Since the data is pre-collected, secondary research conserves time, efforts, and resources. But it also has to be thoroughly analyzed to ensure that the information is sound, current, and applicable to your subject.
So, understanding how secondary data works is really important when you are exploring the difference between primary and secondary research. As all the mechanisms and processes of secondary data is completely different from primary research. So, let us find out more about it.
Common Sources of Secondary Research
There are numerous sources of data collection in secondary research. These sources are very diverse and cater to qualitative and quantitative data requirements.
1. Books
Books are classic yet very important sources. They give elaborate explanation, theories, and historical facts that allow you to comprehend the history of a subject.
2. Academic Journals
The best place to find recent research is in journals. They consist of peer-reviewed reports, experiments, and opinion pieces.
3. Research Reports
Market, health, technology, social issues, and other reports are frequently released by organizations, institutions, and companies. So, such reports can be helpful as they give reliable and factual information.
4. Websites
General information can be accessed easily by sites, blogs and educational platforms. But, you should be selective of sources as they can provide wrong or biased information.
5. Databases
Structured information, statistical data, and past research work is available on online databases like Google Scholar, PubMed, JSTOR, and government archives.
So, all of these sources make secondary research extremely accessible and easy for researchers and students to use.
Example of Secondary Research
One of the clear examples of secondary research is when a researcher uses government health reports to study about the disease trends.
For instance, one can just use the data published by the health department in order to know how the rates of diabetes have varied in the past five years.
See? As simple as that.
Please note, the information already existed here. And this is the key feature of secondary research that you need to remember when studying about the difference between primary and secondary research.
Advantages of Secondary Research
Secondary research has a number of good advantages particularly in academic and business research.
The most popular ones are listed below:
1. Cost-Effective
In secondary research, you do not have to worry about expensive surveys, experiments, or other data collection methods.
As the data already exists, the cost is automatically saved.
2. Saves Time
Obviously, when you do not have to spend your time conducting research. You save a lot of your time, too. So, it’s definitely a win-win. And your research takes less time to complete.
3. Wide Range of Information
Here, you do not have to rely on a single source of information. But you have the Pandora box. Hence, access to information is unlimited.
4. Easy for Beginners
If you are a beginner, then secondary research is definitely the right method for you. All you need to do is find the right research and not do it by yourself.
These benefits definitely makes it a crucial part of the academics.
Limitations of Secondary Research
I know, secondary research might seem like an ideal one for you. But remember, it is not free from limitations. Here are some for you to keep in mind:
1. May Be Outdated
Some of the publications are several years old. So, they do not represent current trends or issues.
2. Possible Bias
Writers or agencies can deliver facts in a manner that favors their personal views or interests.
3. Not Always Specific
The secondary data, most of the time, is gathered in a general sense. And therefore, it might not necessarily respond to your precise research question.
4. Quality Varies
Not every online source can be considered reliable. You have to verify the authenticity of websites, authors, and publications.
Due to these limitations, a number of researchers use both primary and secondary sources to have better and more reliable outcomes.
Key Difference Between Primary and Secondary Research
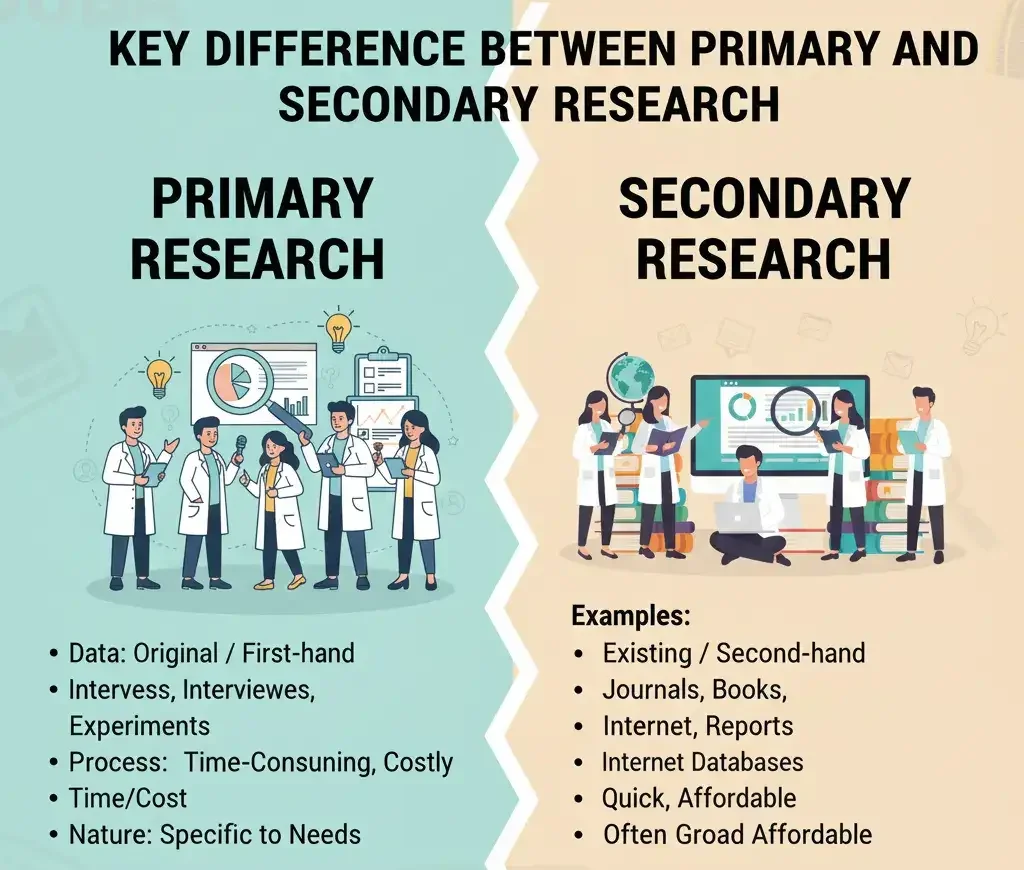
If you really want to see the difference between primary and secondary research, you must examine how each method of research obtains data. Time and money are involved in the research process. And the level of control the researcher has over the whole process.
Although these two methods are both applied to academic research methods, they are completely different in their working process, level of reliability. And areas where you apply them.
I know, it is getting confusing. But do not worry, I know the easiest way to spot the difference between primary and secondary research right away. We will explore examples of primary and secondary data to understand them better.
So, let us start.
1. Data Source
The source of the data is one of the largest difference between primary and secondary research. This is where the information originates.
Primary Research
As we all know by now that primary research only uses firsthand information. That means the information and is new and original.
Hence, the data is directly obtained from the people, events or experiments. As it is first-hand information, it tends to be more precise and focused on a specific research question.
Example:
Interviewing students in a university to know their difficulties in learning online.
Secondary Research
Now, let us take a look at data source of secondary research.
So, the secondary research involves the utilization of existing data. This means that the information has been collected and published by another person. Thus, you just collect, read and interpret it.
Example:
Investigating population patterns using published scholarly articles or government census reports.
So, the primary research means brand new data. While secondary research means existing data. This is the main difference between primary and secondary research
2. Cost and Time
The next key difference between primary and secondary research is the amount, effort, and energy required to complete them.
Primary Research
Well, primary research is definitely more expensive and time-consuming. As the researcher collects all the information by themselves. Thus, it usually requires:
- planning
- designing questionnaires
- looking for participants
- conducting interviews or surveys
- assessing the results
All of this will consume a lot of time and even money, particularly when there is the use of tools, travel or software. So, that is why it is a challenge for students as they have limited deadlines or budgets.
Secondary Research
If we compare it to primary research, then Secondary research is definitely more economical and quicker, as the information is already available. So, you just search, read, and analyze the available sources. That’s it.
Thus, most of the secondary data is free, accessible, and organized. Hence, making it perfect for basic research or literature reviews when time is short.
So, no matter the difference between primary and secondary research. You will always have to choose your method depending on your goals and not the cost.
3. Control and Accuracy
Another big difference between primary and secondary research is control and accuracy. Like To what extent do you have the freedom to influence the research? What is the validity of the information?
Primary Research
It offers the maximum control to the researcher. You will have control over every single step, including:
- What to ask?
- Who to ask?
- How to ask?
- What tools to use? etc.
Due to such control, the data accuracy and relevance are generally greater. So, you just collect exactly what you need specifically. Not something less or more.
Secondary Research
In secondary research, the information is already present. You have no control over how it was gathered or those who took part. You have to trust the accuracy and truthfulness of the primary source.
So, secondary data can sometimes be incomplete, outdated or even biased. But if you choose your sources wisely, it can be really useful. Sources like academic journals, government department reports, or research organizations are highly credible.
This crucial difference between primary and secondary research usually directs the researcher in selecting the appropriate method depending on their objectives.
4. Examples Comparison Table
I know, this must be confusing for you. That is why I have prepared a simple comparison table to help you understand the difference between primary and secondary research in a clear manner. So, let us take a look at how these two research methods differ from one another:
| Aspect | Primary Research | Secondary Research |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | The researcher collects the data firsthand. | The data already exists and has been collected by other people. |
| Cost | The cost is high | Cost is low |
| Time | It takes more time to complete | Time duration is less due to availability of data |
| Accuracy | Highly accurate | It depends on the quality of the data source |
| Example | Surveys, interviews, experiments | Academic journals, government reports |
Thus, this table helps you in quickly understanding how both methods vary over various factors like cost, time, and reliability.
How These Differences Affect Research Decisions
I am sure that you must be clear about the difference between primary and secondary research by now. And it won’t be hard for you to choose the right method for your study.
But always remember that these differences affect your research decisions critically. For instance:
- To get up-to-date, specific, and correct information, primary research is the best option for you.
- If you need a quick information on a topic or historical data, then secondary research is the better option.
- In most academic research techniques, researchers rely on both primary and secondary sources of data to reinforce their results.
So, s combination of both approaches is useful. As it offers a balanced view, since primary data offers depth, whereas secondary data offers context.
Advantages and Disadvantages
In the world of research, you cannot just name a specific technique to be the best. But the best technique depends on the type of research and your research goals.
So, it is not fixed. But you choose it as per your needs. That is why it is really important for you to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each type. We now know the difference between primary and secondary research. Let us shed some light on the pros and cons of each type to make the right choice always.
Advantages of Primary Research
Primary research is a highly esteemed type of research in academic and professional research work. It provides original data and firsthand data to the researcher. Thus, here are its key advantages:
1. Authentic and Accurate Data
The data is original because you collected it by yourself. And they are reliable and directly connected to your research question. Hence, making your results increasingly credible.
2. Specific to the Research Goal
Primary research enables you to tailor-fit the questions to meet your precise needs. You decide what to ask, who to ask, and the mode of gathering the data.
3. Offers Full Control
You are in charge of all the steps, data type, participants, tools, and environment. Hence, this makes it consistent and less likely to make mistakes.
4. Useful for Unique or New Topics
Primary research provides the most current information in the market when you are researching a modern trend, a new product, or a particular group of people.
Disadvantages of Primary Research
Now, let us turn the coin and talk about the disadvantages of primary research:
1. Costly
Primary research may involve expenditure on surveys, travel, printing materials or software. Hence, this might not be the best option to students with restricted budgets.
2. Time-Consuming
It can be time-consuming to design questionnaires, collect information, and analyze the results. And I am not talking about few days. But it can take weeks or even months.
3. Requires Skills and Planning
You have to understand how to write good questions, sample groups properly, and conduct good research. So, it requires expert skills.
Now, you better consider both pros and cons of primary research before choosing it for your next study.
Advantages of Secondary Research
The popularity of secondary research is due to its ease, speed, and availability. Let us take a look at some of its key benefits:
1. Cost-Effective
The majority of the secondary data is free or cheap. Data is readily available in books, journals, reports, and websites without the burden of financial implication.
2. Saves Time
Since the information is already there, you just have to search it and interpret it. So, it reduces the duration of the research.
3. Wide Range of Sources
There are various reliable sources of information that you can use. For example, journals, reports, databases, academic websites, and government publications.
4. Ideal for Early Research Stages
Secondary data helps in the background knowledge or hypothesis formulation to be used in primary research.
Disadvantages of Secondary Research
Despite being easy and convenient, secondary research has some weaknesses:
1. Limited Accuracy
The way the data was collected is beyond your control. In case the original writer is not correct, you would be using incorrect information without knowing.
2. May Be Outdated
Reports or articles might be many years old. In the case of rapidly evolving subjects, outdated information may result in poor conclusions.
3. Not Always Relevant
Secondary data is typically general. It might not best fit your research question as it was gathered to do otherwise.
So, knowing these strengths and weaknesses, and difference between primary and secondary research will assist you to make the right decision. You will know when you can use primary data, when to utilize secondary data. And when to adopt a mixture of both techniques to achieve the desired outcome.
Combining Both Methods
A lot of researchers combine primary and secondary research within one project, as both methods have something to offer.
So, this amazing combination is commonly referred to as triangulation or the mixed-methods approach. It involves the application of disparate data in order to verify findings and make more robust and credible results.
What Is Triangulation?
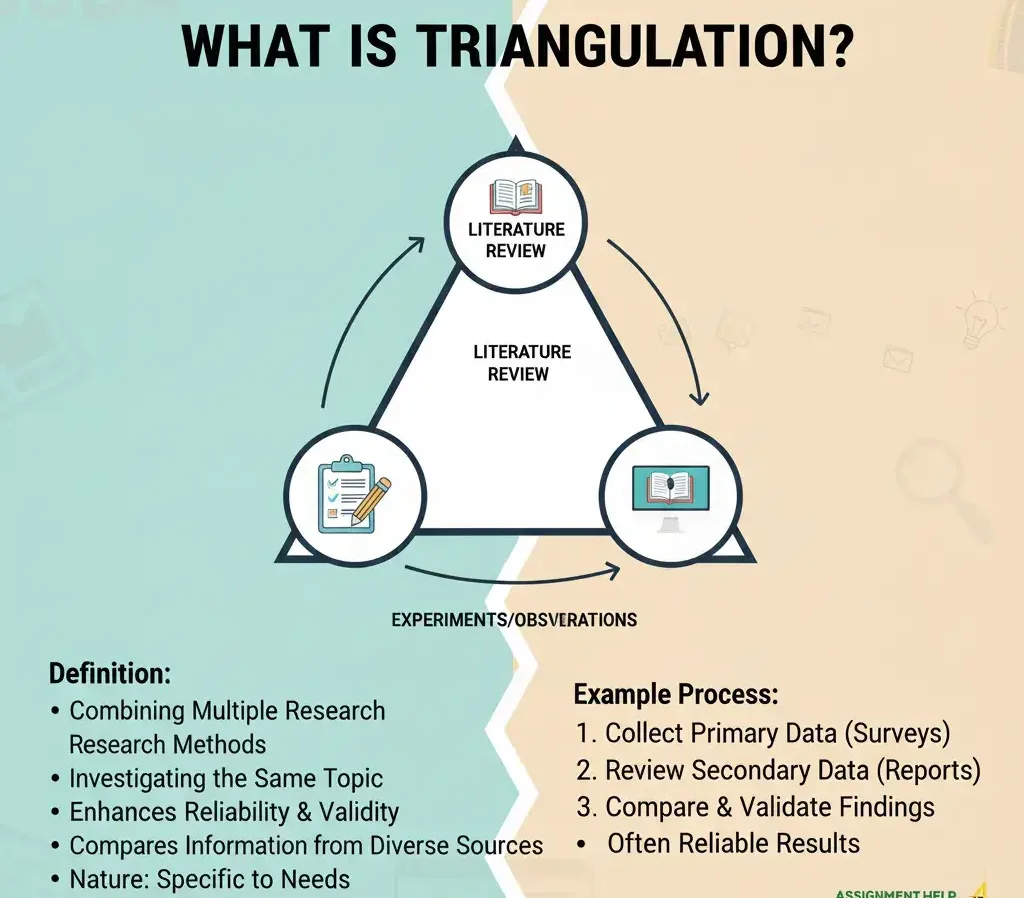
Triangulation is an approach where more than one method is used to research the same topic.
So, you do not use surveys alone or books alone, but you combine them. This makes it more accurate since it assists you in comparing the information from various sources.
For instance:
- You are collecting primary data by means of surveys or interviews.
- After that, you validate or benchmark that information with published reports or articles.
So, this mixed process helps make your results more reliable and balanced.
How Mixed Methods Strengthen Research
In case you are wondering, let me tell you that the mixed method approach is one of the best with various benefits. Also, it can help you strengthen your research. Here is how:
1. Complete Perspective
This research can help you get a whole 360 degree perspective of your topic.
So, the primary research provides you with profound, detailed, and new information. The secondary research provides you with a general background. Thus, when used together, they make you see the big picture.
2. More Reliable Findings
When the primary data and secondary data lead you to the same result. Then that means you have stronger and more valid results.
3. Saves Time with More Accuracy
Secondary research will help you to know the current trends and then concentrate on your primary research to address the gaps.
4. Supports Both Qualitative and Quantitative Data
When we talk about a mixed approach. It is not just about anyone specific approach anymore. But it helps you gather both qualitative and quantitative data.
Hence, adding balance to your research. And making it more meaningful with a hint of professionalism.
Why Combining Both Methods Is the Smart Choice?
Now, that’s a smart question to ask.
Well, in academic research methods and professional projects, it is not always sufficient to work only with one type of data.
Primary research is genuine but expensive and time-consuming.
However, secondary research is convenient yet not always up to date.
So, the integration of the two gives you the precision of primary data and the pace of secondary data. Thus, making you come up with strong, well-balanced results.
FAQs
Students usually share the same questions when researching the difference between primary and secondary research.
So, to make you get to know more about both approaches, some simple and straightforward answers are listed below. Here we go:
Q. What is an example of primary research?
Ans: A survey to learn about student satisfaction in your university is an example of primary research. You generate questions, receive answers directly from students and analyze them yourself. It makes it first-hand, original information that was designed to serve your research. Other typical examples of primary sources of data collection are interviews, experiments, and focus groups.
Q. Is a literature review primary or secondary?
Ans: The literature review is secondary research. When writing a literature review, you are reading and analyzing the already existing information – journal articles, books and reports. You are not gathering new information, but you are synthesizing, contrasting, and analyzing past results of other scientists.
Q. Why use secondary data?
Ans: The reason why secondary data is used is that it is fast, convenient and economical. You do not have to create surveys and experiments in order to obtain vast amounts of information within a short period. It can be most useful in creating a background knowledge base, learning trends, and backing your arguments with published material. Secondary research is also practical in situations where primary data is hard or costly to obtain.
Q. Which is more reliable — primary or secondary?
Ans: Primary research is largely regarded to be more credible since the researcher is in control of every aspect and the researcher is the one who gathers data. This renders it correct, precise and study-specific. Nonetheless, secondary data may also be credible in case it is issued by any reputable organization like academic journals, government databases, or well-known research agencies. The credibility lies with the selection of sources.
Q. Can I mix both in one project?
Ans: You can, yes, and in most cases, you should. The blend of the two research methods, primary and secondary, assists you in developing more robust and comprehensive results. The advantages of this mixed-method or triangulation design are that you are able to compare various sources of data and validate your findings and develop a balanced study. Numerous academic research methodologies would advise students to take a combination of both so that they can analyze more.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, understanding the difference between primary and secondary research is crucial for any researcher to produce a meaningful piece of work.
So, these two techniques are strong in their respective manner. Each one of them has a unique role to play in academic research techniques, business studies, and in daily decision-making.
Well, the Primary research provides new, original, and very specific data. And secondary research provides you with fast access to the already existing data that also helps you see the big picture.
Thus, when you are choosing between the two, you must consider your research objectives, time, and resources. I am sure that you know primary research is preferable to secondary research in case you require first-hand information, recent discoveries, or data that is specific to your topic.
However, when you require background information, theoretical reinforcements, or a less expensive means of obtaining information. Then, secondary research will be of good use to you.
But the twist is that many researchers use the combination of both sources to create the strongest results.
Primary research is authentic and deep. Whereas secondary research is contextual and time-consuming. So, they will assist you in developing a balanced study that is accurate, comprehensive, and credible.
Hence, ultimately, it is not about the selection of one method over the other. But rather knowing when one method is an appropriate fit over the other.
Thus, knowing the difference between primary and secondary research. That includes data collection sources to benefits and drawbacks will help you to create a more informed, reliable, and effective research.
Best of Luck!

